Abstract
Background: We have previously shown that fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) can protect both chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells with FLT3 internal tandem duplication (FLT3-ITD) from tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in a paracrine fashion (Traer et al. Blood 2014, Traer et al. Cancer Res. 2016). FGF2 expression increases in marrow stroma during treatment with TKIs and leads to expansion of FGF2-expressing stromal cells through autocrine stimulation of FGF receptor 1 (FGFR1). This results in more cells to provide paracrine protection for leukemia cells. However, the mechanism by which FGF2 is secreted from stromal cells remains unclear since FGF2 does not have a signal peptide.
Results: We used two related human stromal cell lines to study FGF2 secretion. HS-5 strongly expresses FGF2 and is protective of CML and FLT3-ITD AML cell lines (K562 and MOLM14, respectively). The related HS-27 cell line expresses little FGF2 and is less protective. HS-5 conditioned media was ultracentrifuged at 100,000g to separate soluble proteins from extracellular vesicles (ECVs). FGF2 was primarily associated with ECVs. Multiplex ELISA was used to analyze 30 cytokines in the soluble fraction and the ECV pellet, and only FGF2 was selectively enriched in ECVs. We then separated ECVs into exosomes, larger microvesicles and apoptotic bodies by sucrose step-gradient and found that FGF2 was most highly enriched in exosomes, along with the exosome markers CD9 and tsg-101. The size of exosomes was confirmed by electron microscopy. Fluorescently labeled HS-5 exosomes were found to be endocytosed by K562 and MOLM14 cells using confocal microscopy. HS-5 exosomes were highly protective of K562 and MOLM14 treated with TKIs, and more protective than soluble proteins.
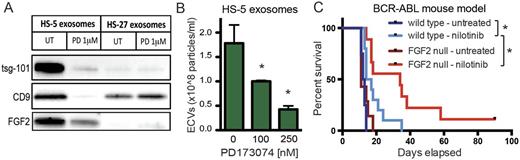
We compared exosome production from HS-5 and HS-27 cells and found that HS-5 cells produced significantly more exosomes (p<0.01). This suggested that FGF2-FGFR1 autocrine signaling may regulate increased production and secretion of FGF2-containing exosomes. The FGFR inhibitor PD173074 significantly reduced secretion of exosomes from HS-5, but not HS-27 cells (Figure 1A,B), and altered the morphology of HS-5 cells (p<0.01). Silencing of FGFR1 in HS-5 cells by siRNA, shRNA and CRISPR also significantly reduced exosome production. Cultured primary stromal cells from wild-type and FGF2 null mice displayed a similar trend: exosome production was significantly higher in wild-type stroma, and FGFR inhibitors only reduced exosome production in wild-type stroma (p<0.05).
These results suggest that FGFR inhibition overcomes protection in two ways: 1) by blocking the paracrine protective effect of FGF2-containing exosomes on leukemia cells and 2) by reducing secretion of FGF2-containing exosomes. To evaluate the direct effect of FGFR inhibitors on stromal cells, HS-5 cells were pre-treated with PD173074 for one week to fully suppress FGFR1 signaling and then PD173074 was removed prior to collecting conditioned media (CM). CM from PD173074 pre-treated HS-5 cells was significantly less protective of MOLM14 cells treated with FLT3 inhibitors (p<0.001) than comparable CM from untreated HS-5 cells.
We then tested the role of FGF2 in the leukemia microenvironment using a mouse model of leukemia. FGF2 +/+ and -/- mice were transplanted with FGF2 +/+ bone marrow that was retrovirally transfected with BCR-ABL. Mice treated with the BCR-ABL inhibitor nilotinib survived significantly longer in the FGF2 -/- background (p=0.028), providing further evidence that stromal FGF2 protects leukemia cells from targeted kinase inhibitors (Figure 1C).
Conclusions: Marrow stromal cells secrete FGF2 in exosomes, which are subsequently endocytosed by leukemia cells and promote survival of leukemia cells after TKI treatment. In addition, FGF2-FGFR1 autocrine signaling in stromal cells expands the number of FGF2-expressing cells as well as the secretion of FGF2-containing exosomes. This FGF2-mediated reprogramming of the marrow microenvironment enhances paracrine protection of residual leukemia cells during TKI therapy. However, FGF2-mediated reprogramming of marrow stroma can be reversed by FGFR inhibitors, making the leukemia microenvironment a therapeutic target for combination therapy.
Traer: Notable Labs: Equity Ownership; Tolero: Consultancy; ImmunoGen: Consultancy. Druker: Novartis: Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aptose Biosciences: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Monojul: Consultancy; Beta Cat: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MolecularMD: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GRAIL: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oregon Health & Science University: Patents & Royalties: #843 Mutated ABL Kinase Domains (licensed to various companies); #0996 Detection of Gleevec Resistant Mutations (licensed to various companies, including MolecularMD); #0606 Treatment of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (exclusively licensed to Novartis); McGraw Hill: Patents & Royalties; Third Coast Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Baxalta US Inc.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; CTI Biopharma: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MED-C: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche TCRC: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ARIAD: Research Funding; Henry Stewart Talks: Patents & Royalties; Millipore: Patents & Royalties: Royalties from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, which has an exclusive commercial license with Millipore for monoclonal antiphosphotyrosine antibody 4G10, which I developed while employed at DFCI.; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cylene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society: Other: Joint Steering Committee of AML Master Protocol, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal